
Regardless of the total delay time, RTMP should deliver a smooth playback experience with parallel audio and video output synced to the same timing information. Factors like network connectivity, video resolution, added audio layers, speed of the transcoding server, and the playback device’s download speed all affect the latency of an RTMP stream. Those speeds may not be sufficient for uses like two-way video calling, which must be perceived as instantaneous, but they’re satisfactory to deliver hosted content and even for most one-way live streams.
With a delay time from input to delivery of about 3-5 seconds, RTMP is reasonably fast even by today’s standards. The Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) is a standardized set of specifications developed to transmit streaming audio, video, and data from a source to a user’s playback device over the internet, with synchronized timing and low latency.

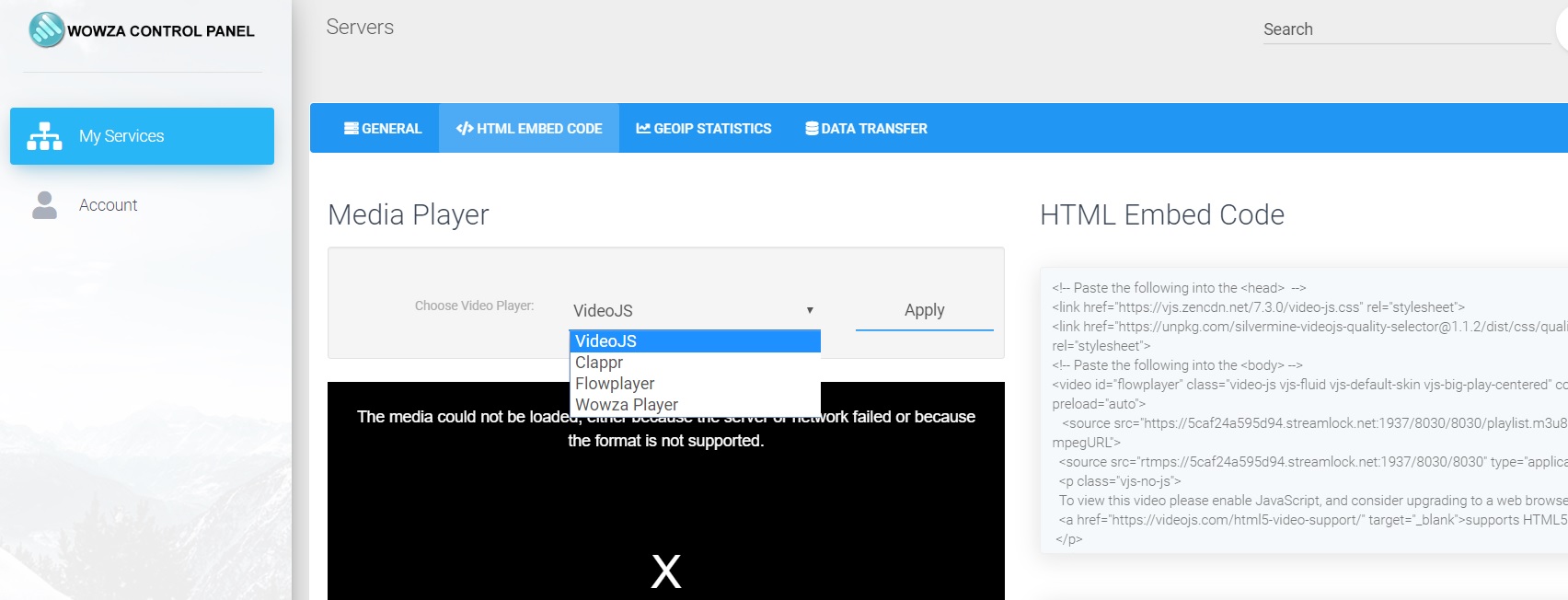
#Rtmp html5 code
Looking for a more technical code tutorial instead? Check out our step-by-step guide to building a live stream with Mux, Stream, and Flutter→ What is the Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP)? All of these platforms rely on the foundational streaming architecture and concepts that RTMP standardized, so it’s worth reviewing those concepts before you start to build a live streaming platform.
#Rtmp html5 how to
Today’s developers may not need to know every detail of how to build a traditional RTMP stream from initial capture to delivery - but a high-level understanding of how the RTMP framework functions is critical to building and maintaining any modern app or platform designed to deliver synchronized audio, video, and data to end users. These newer protocols gained popularity with the decline of Flash support and the rise of streaming platforms outside the traditional web browser, including mobile and desktop native apps as well as smart TVs and some IoT devices. And although newer streaming protocols like HLS and MPEG-DASH are now used for the content distribution stages of the streaming pipeline, RTMP still plays an important backend role (more on what that looks like below).

When Macromedia launched the Real-Time Messaging Protocol in the 1990s as the backbone of Flash, it established what would become the near-universal standard for multimedia streaming over the internet for more than 20 years.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
